Images real and virtual. An object is placed in front of a converging lens with a focal length of 20cm.
 Chapter 34b Reflection And Mirrors Ii Analytical Ppt Download
Chapter 34b Reflection And Mirrors Ii Analytical Ppt Download
describe sign convention for real and virtual image
describe sign convention for real and virtual image is a summary of the best information with HD images sourced from all the most popular websites in the world. You can access all contents by clicking the download button. If want a higher resolution you can find it on Google Images.
Note: Copyright of all images in describe sign convention for real and virtual image content depends on the source site. We hope you do not use it for commercial purposes.
Real images occur when objects are placed outside the focal length of a converging lens or outside the focal length of a converging mirror.
Describe sign convention for real and virtual image. Lateral magnification formula and image height 8. Sign convention di do f hi ho and m. When you look in the mirror you an image of yourself.
When measuring the height of an inverted image using the cartesian sign convention where the x axis is the optical axis the value for h i will be negative and as a result m will also be negative. E is the object place where good the image be if the object is moved 20 cm towards the mirror state reason. There are some more differences between a real and a virtual image that will be discussed in this article.
If you insert your hand near the real image the hand will get burned because the light rays from the source actually converge at the point of the real image. Convex lens ray diagram real or virtual image. April 19 2011 posted by olivia.
Describe sign convention for real and virtual image ask for details. A real image is illustrated below. A real image is an image formed by actual rays of light.
Difference between virtual and real images. Show more show less. A400cm b20cm c10cm 2.
For each object distance find the image distance and the magnification. If you manage to insert your hand to the point of the virtual image your hand wont burn because there are no light rays over there and sometimes there is a wall. The image of an object formed by a mirror is real inverted and is of magnification 1 is if the image is at the distance of 40 cm from the mirror wher.
From p the distance opposite to incidence ray is measured in negative. Sign conventions for spherical mirrors image formation in concave mirror from p the distance in the direction of incident ray the measurement is taken positive. Is that image real or virtual.
Watch this video to know more about real and virtual images. Describe whether each is virtualuprightrealinvertedreducedor enlarged. An image such as that seen in a mirror in which the rays of light appear to be emanating from some object that isnt there is called a virtual image.
Real images are always inverted and they may be either larger or smaller than the object. Real images are those where light actually converges whereas virtual images are locations from where light appears to have converged. However the traditional sign convention used in photography is real is positive virtual is negative.
An object is placed in front of a diverging lens with a focal length of 200cm. To access the entire course of reflection and. Virtual images are made by rays that do not actually come from where one sees the image.
 Lecture 14 Images Chp 35 Opening Demo Topics Plane Mirror Two
Lecture 14 Images Chp 35 Opening Demo Topics Plane Mirror Two
 Lecture 14 Mirrors Chapter 23 1 23 3 Outline Flat Mirrors
Lecture 14 Mirrors Chapter 23 1 23 3 Outline Flat Mirrors
 Optics Lecture 2 Book Chapter 34 Ppt Video Online Download
Optics Lecture 2 Book Chapter 34 Ppt Video Online Download
What Is The Sign Conventions For Concave Mirror And Concave Lens
 Optics Lecture 2 Book Chapter 34 Ppt Video Online Download
Optics Lecture 2 Book Chapter 34 Ppt Video Online Download
 Describe Sign Convention For Real And Virtual Image Brainly In
Describe Sign Convention For Real And Virtual Image Brainly In
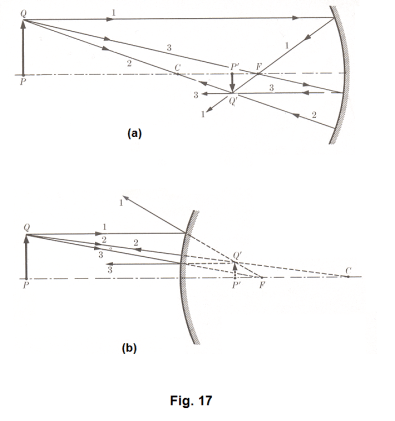 Real And Virtual Images Image Formation By Lenses Plane Mirrors
Real And Virtual Images Image Formation By Lenses Plane Mirrors
 List The New Cartesian Sign Convention For Reflection Of Light By
List The New Cartesian Sign Convention For Reflection Of Light By
 Converging Lens Image Real Or Virtual Youtube
Converging Lens Image Real Or Virtual Youtube
Image Formation By Concave Mirrors
